Difference between revisions of "ROSA Installation"
(translated from Russian) |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Message|This guide describes installation of ROSA 2012 LTS but most of its parts equally apply to ROSA 2011, with only differences in appearance}} | ||
| + | |||
'''ROSA''' is an operating system aimed to be as closed to users as possible. That's why its installation process is very simple: you should just download installation file, write it on some media (CD or flash), reboot the system and launch the installation wizard. To make working with the wizard even more easier, we have prepared this step-by-step guide. | '''ROSA''' is an operating system aimed to be as closed to users as possible. That's why its installation process is very simple: you should just download installation file, write it on some media (CD or flash), reboot the system and launch the installation wizard. To make working with the wizard even more easier, we have prepared this step-by-step guide. | ||
Revision as of 16:11, 26 April 2012
ROSA is an operating system aimed to be as closed to users as possible. That's why its installation process is very simple: you should just download installation file, write it on some media (CD or flash), reboot the system and launch the installation wizard. To make working with the wizard even more easier, we have prepared this step-by-step guide.
Preparing bootable flash drive
If you want to prepare a bootable flash drive using ROSA ISO image, you can do this in either graphical or text mode.
Graphical mode
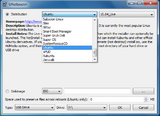
To prepare a bootable drive in graohical mode, install the unetbootin package from your repository. If you are using Windows(TM) then you can download the tool from the official site.
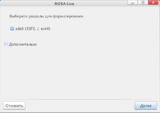
Choose "Diskimage" and press the "..." button to choose ISO image. Then in the "Drive" section select a letter corresponding to your flash drive and press "OK".
After the bootable flash drive is created, log out from the system and reboot without ejecting your flash drive from USB.
Text mode
In order to prepare a bootable flash drive in text mode, use the dd utility (available in Linux only) with bs=1MB option, such as:
dd if=ROSA.iso of=/dev/sdb bs=1MB
where ROSA.iso - is an iso image you have downloaded and /dev/sdb - is a path to flash drive device. You can know this device name by examining output of the following command:
df -h
Installing ROSA
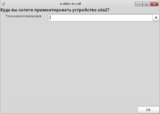
- When the bootable flash drive is ready, reboot your machine and in the appeared menu choose "Install system". Installation wizard will appear.
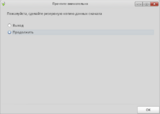
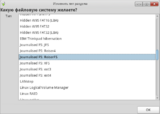
- First, you will see a disk partitioner window. Choose "Manual" and press "Next".
- Press the "Toggle to expert mode" button. Choose a partition for your Linux system.
Novice users are often confused by the disk partitioning. Unlike Windows where a single large partition is enough, Linux can require more complex partitioning in some situations. Though it is possible to install Linux on a single partition, as well, it is recommended to have at least separate swap and root partitions (the latter is designated as /). But how much space should every of this partitions occupy? There is no single solution for this, but below we'll provide you with recommended numbers for ROSA.
For the most purposes, two partitions are enough:
1. A root partition (/) for the core system - approx. 15 Gb. Choose either ext3 or ext4 type for this partition. Ext4 should be faster in some situations, though there are some aspects that are out of scope of this guide.
2. A swap space - often set to the size of your RAM.
You can also create a separate home partition where all your personal data (documents, photos, etc.) will be stored. This is not necessary; you may for example use Windows partitions for these purposes. If you don't create a separate partition then a special folder called 'home' will be created in the partition where the main part of the system is installed. In our example, we will use the default pasrtitioning.
Now you should have two partitions.
Press the "Mount point" button.
- Press "Type". choose the filesystem to be used (Ext4 is used by default).
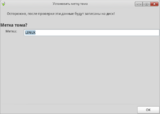
- For convenience, we recommend to assignd a label to the ROSA partition. This will allow file managers to display meaningful name for that partition. Press "Label" and enter any label you want using Latin characters only.
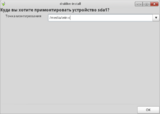
- Now let's set parameters to be used when mounting the partition. Press "Parameters" and select only the user option (all the others will be "turned on" automatically), and press "ОК".
- When disk partitioning is done, press "Next". You will be suggested to format ROSA partition. Let's agree with this and press "Next".
- Installation of the system will be started.
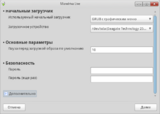
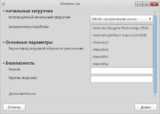
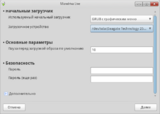
- Now when all packages are installed you should configure the Grub bootloader.
- Now press "Finish".
- Bootloader has been installed successfully. Now the system is installed on your hard drive. Press "Finish".
- After reboot, set a password for root and add a user. Now your ROSA installation is completed.